Imagine a mobile phone charger that doesn’t need a wireless or mains power source. Or a pacemaker with inbuilt organic energy sources within the human body. Well, now they’re one step closer…
Australian researchers led by Flinders University are picking up the challenge of ‘scavenging’ invisible power from low-frequency vibrations in the surrounding environment, including wind, air or even contact-separation energy (static electricity).
“These so-called triboelectric nanogenerators (or ‘TENGs’) can be made at low cost in different configurations, making them suitable for driving small electronics such as personal electronics (mobile phones), biomechanics devices (pacemakers), sensors (temperature/pressure/chemical sensors), and more,” said Professor Youhong Tang, from Flinders University’s College of Science and Engineering.
Further research aims to further develop this renewable form of energy harvesting by designing simple fabrication from cheap and sustainable materials, with high efficiency.
“They can use non-invasive materials, so could one day be used for implantable and wearable energy harvesting aims,” detailed Flinders Institute for NanoScale Science and Technology PhD candidate, Mohammad Khorsand, co-lead author on recent papers in international journal Nano Energy.

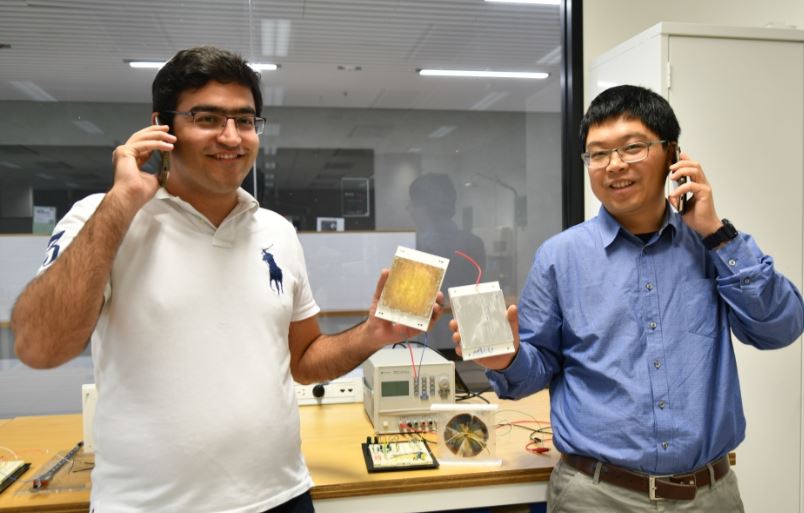
Professor Tang and Mr Khorsand, front, with fellow researchers Jeetendra Chhetri and Steven Wang at the Tonsley nano-engineering lab. Image credit: Flinders University.
The latest paper uses artificial intelligence (AI) enhanced mathematical modelling to compare the function of the number of segments, rotational speed and tribo-surface spacing of an advanced TENG prototype to optimise the storage and performance.
The researchers, with colleagues at the University of Technology Sydney and elsewhere, are working to improve power generation of TENGs and store the generated power on a supercapacitor or battery.
“We have been able to effectively harvest power from sliding movement and rotary motion which are abundantly available in our living environment,” said Professor Tang.
The latest paper, Artificial intelligence enhanced mathematical modeling on rotary triboelectric nanogenerators under various kinematic and geometric conditions (2020) by Mohammad Khorsand, Javad Tavakoli (University of Technology Sydney), Haowen Guan and Youhong Tang has been published in Nano Energy (Elsevier) DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104993
Also see 2019 paper Simulation of high-output and lightweight sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerators DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104115
Key highlights:
- The first generation of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) was fabricated at Georgia Institute of Technology in the US about 10 years ago.
- Research at Flinders University is aiming design cost-effective and high-efficient sliding and rotary TENGs for further development and possible commercialisation.
- This research on the next generation of TENG is using AI and simulation modelling to reduce the cost of repeating the experiment for various conditions.
- The research team is focusing on numerically predicting the outputs of TENGs by measuring their voltage, current, power and energy under various electric specifications and geometries of dielectric films.












